Materiality Assessments
Materiality Assessment
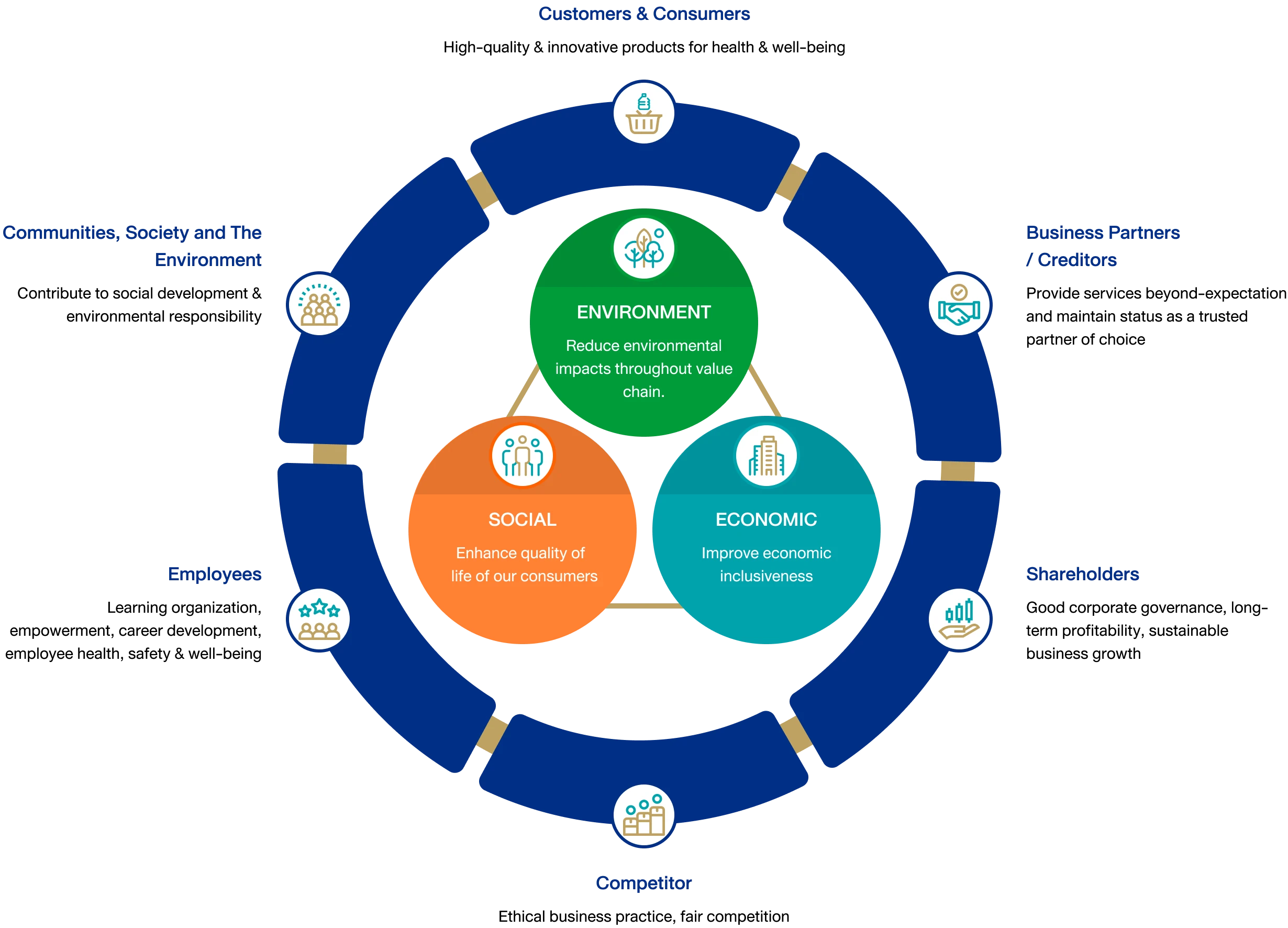
In addition to setting development goals and key performance indicators (KPIs), both of which empower organizations to use their full potential, Osotspa believes that identifying and prioritizing the major issues which affect the organization and its stakeholders is critical to shaping our business across economic, social, environmental, and governance aspects
We thus conduct materiality assessments in accordance with the GRI Standards to ensure that our business takes into consideration the changing economic, social, and environmental contexts. Our materiality approach consists of 5 steps that are repeated in the same order for each reporting cycle.
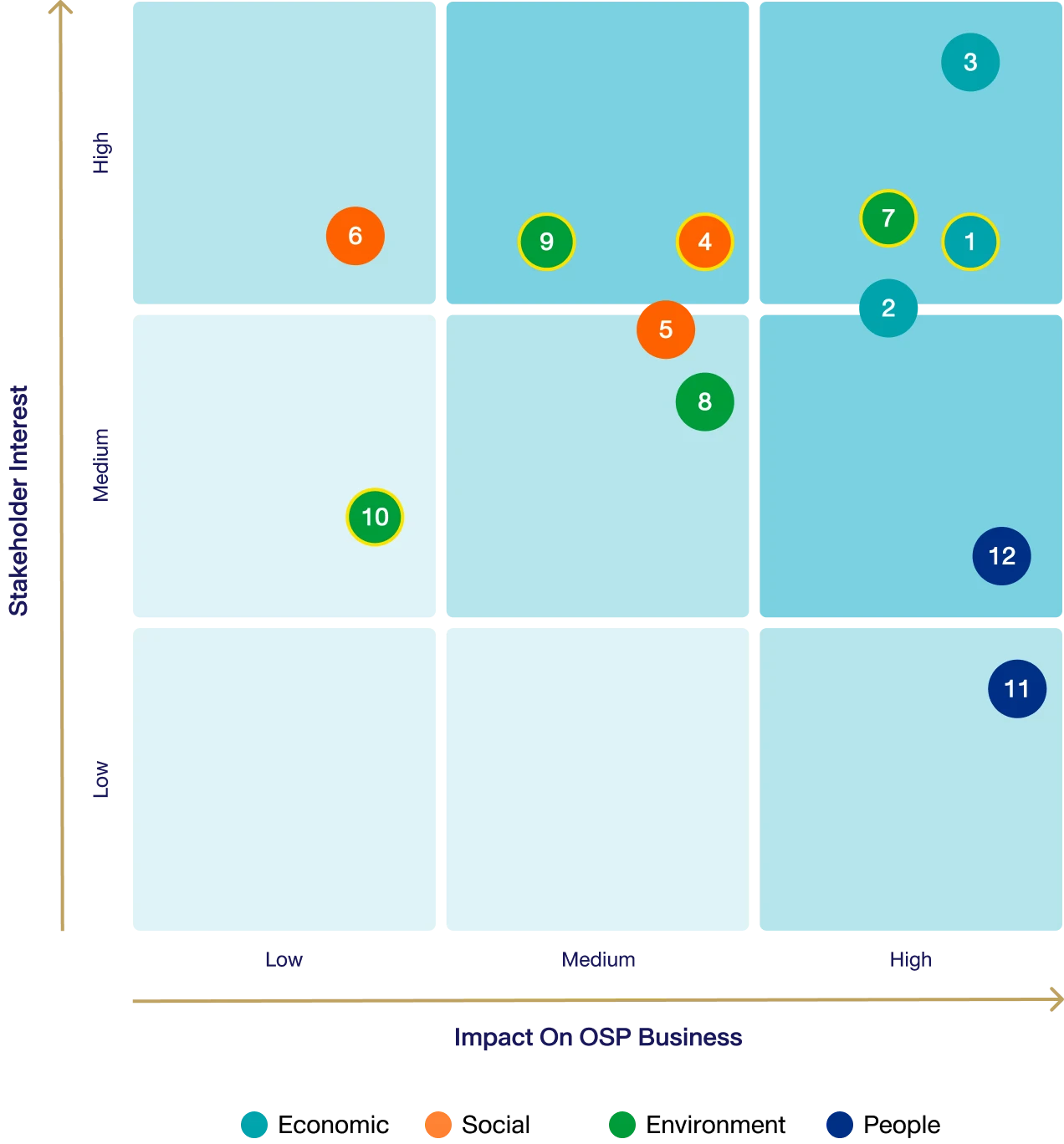
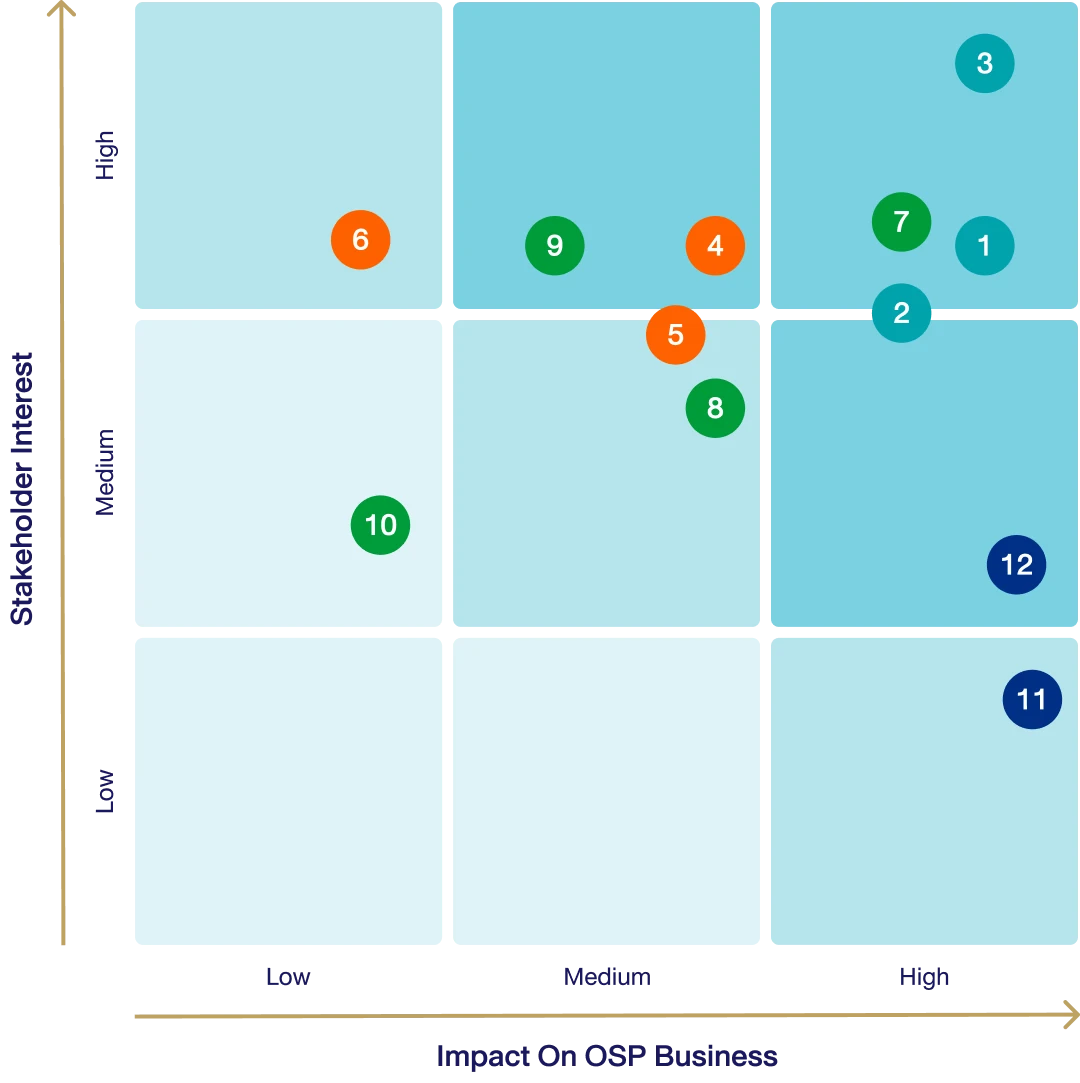
Top Materiality Issue
-
1Supply Chain Management
-
4Consumer Health & Well-being
-
7Energy & Climate Management
-
8Water and Wastewater Management
-
9Sustainable Packaging
-
2Supply Chain Management
-
3Product Quality & Safety
-
5Responsible Communication & Product Labelin
-
6Corporate Citizenship & Philanthropy
-
10Waste Management
-
11Human Capital Development
-
12Labor Practice
Materiality analysis is conducted and reviewed at least annually, based on the principle of double materiality, and incorporates input from both internal and external stakeholders. The Sustainability Department reviews and identifies material topics that may impact the value chain at both global and local levels. These topics are assessed and prioritized through a materiality matrix, considering the average score of likelihood and impact.
The process includes ranking material topics (low, medium, high) and defining relevant boundaries. The results are reviewed by the Sustainability Committee and the Board of Directors, with final approval by the Board. The validated outcomes are used to guide sustainability reporting and disclose key issues relevant to the Company’s business operations and sustainable development.
Furthermore, the material topics identified are integrated into the Company’s Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework to ensure the development and implementation of comprehensive risk management activities.
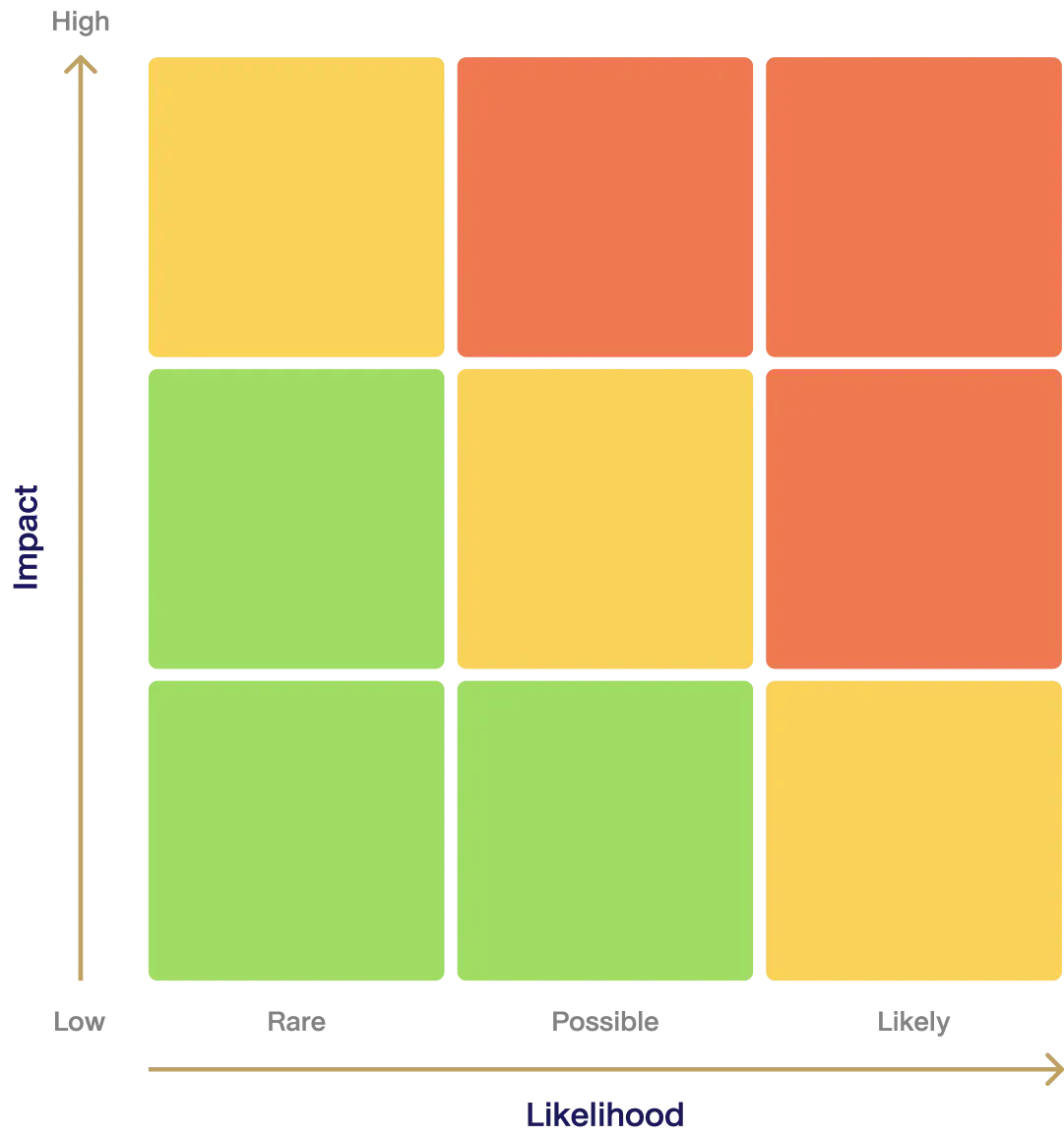
| Likelihood | Rare | Possible | Likely |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Not Happened in 3 Years |
Rarely Happened (1-2 times in last 3 years) |
Already Happened (3 times or more occasions within last 3 years.) |
| Impact | Low | Medium | High |
| Definition | < 100 MB and Other Qualitative Factors | 100-250 MB and Other Qualitative Factors | > 250 MB and Other Qualitative Factors |